Geospatial solutions
We use advanced technology and innovative approaches to accurately capture and display spatial data.
Integrated
management
of geospatial
data.
Integrated geospatial data management
Photogrammetry
Orthophotos and orthophotos
3D reconstructions
Oblique images
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
Classified 3D point cloud
Digital Surface Model (DSM)
Digital Terrain Model (DTM)
Multimodal data
2D and 3D models
360° panoramas and videos
GeoBIM
Virtual reality (VR)
Flycom Technologies
English
Data processing
Modelling, simulation and analysis
Data models
Algorithm development
Utility inspection of infrastructure
Electricity network
Railway network
Road network
Gas pipeline
Data integration
Data aggregation
Databases
Data storage
Photogrammetry

True orthophoto
Advanced digital photogrammetry product that utilizes high-density image capture to georeference and refine images, accurately mapping the tops of buildings, bridges, and other structures. It eliminates perspective distortions, making it a precise foundation for cartography and spatial analysis.
English
Oblique imagery
Special form of angled photography that allows you to view the ground and objects from several angles.
Oblique imagery offers greater accuracy and is a key tool in modern spatial planning.
English
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
Presenting data in a variety of ways to make it easier to understand, analyse and use spatial data.
Comparison of DTM and DSM:


Classified 3D laser point cloud
The raw LiDAR data is represented as a point cloud. By processing these points, they are classified according to their characteristics, which is a crucial step for an accurate 3D representation of terrain, objects and vegetation.
DSM (Digital Surface Model)
Showing the surface elevation with all buildings, vegetation and infrastructure. Important for visualising cities, urban planning and assessing height changes.
DTM (Digital Terrain Model)
Showing the bare height difference of the terrain without objects, trees and buildings. Used for hydrological studies, erosion analysis and engineering design.
Multi-modality data
Our data describe space in different modalities, from 2D cartographic representations, 3D space and 4D simulations.
Geospatial data processing and analysis
Our products and solutions are the result of efficient mass data processing, the use of modern machine learning algorithms and general artificial intelligence.
3D modelling

Flood simulations

Measurements and analysis

Horizontal traffic signalling

Vertical traffic signalling

Damage assessment of road surfaces
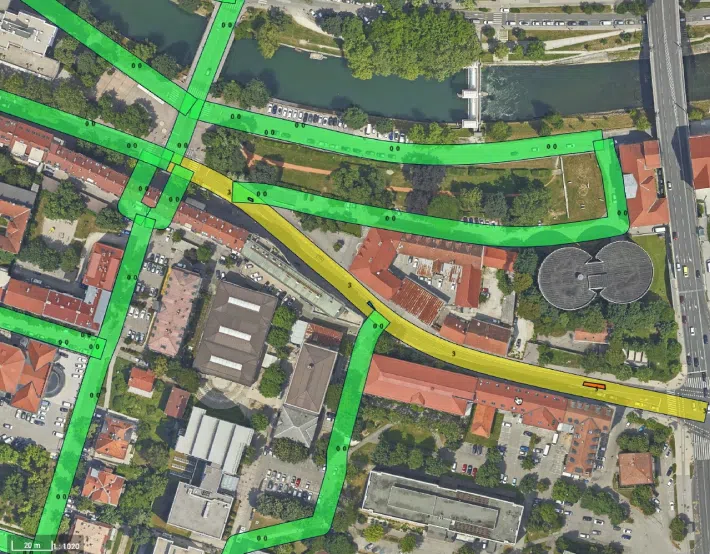
Analysis of flood zones

2D topography

Water image segmentation

Reviews of different infrastructures
Multi-modal capture combining the use of different sensors and technologies,
such as LiDAR, terrmography, UV, IR and RGB.
Data integration
Data integration
Integration of different types of geospatial data, advanced visualisations and comprehensive overview of areas (digital twins).
Advanced tools and analysis
Efficient use and in-depth processing of data within the web platform.
Data distribution
Secure, fast and efficient data availability for all key stakeholders

